Google Analytics ETL with python

0. Intro
Google Analytics is really useful but sometimes you want to retrieve all the data and perform your own analysis and create your reports. In this post you will see how to do that with python.
1. Google permisions and keys
1.1. Get the Google key
The first thing to do is to download the Google key. To do so you only need to follow Google Analytics API steps.
To sum them up you will need to:
- Go to
Google service accounts page.
- Make sure to select the desired project from the navigation bar (at the top).
- Start to create a new service account
- Give it some roles (optional)
- Create a
jsonprivate key - Download that key. It will allow you to access google data
1.2. Enable Google Analytics API
You will need to enable the usage of the Google Analytics API with:
- Go to
API in Google Developers console.
- Make sure to select the desired project from the navigation bar (at the top).
- Click enable
1.3. Allow the user to see Google Analytics data
From the previous step you created and account with an email similar to your_project@your_web.iam.gserviceaccount.com
(you obviously need to change your_web and your_project). Then give it read permisions with:
- Go to
Google Analytics web.
- Select the Admin section from the left bar
- Click
Manage Usersat account level. It is important that you give it at the account level in order to work. - Add the user with the email from the previous step
- Give it read access.
It can take some time until the new user has reading permisions.
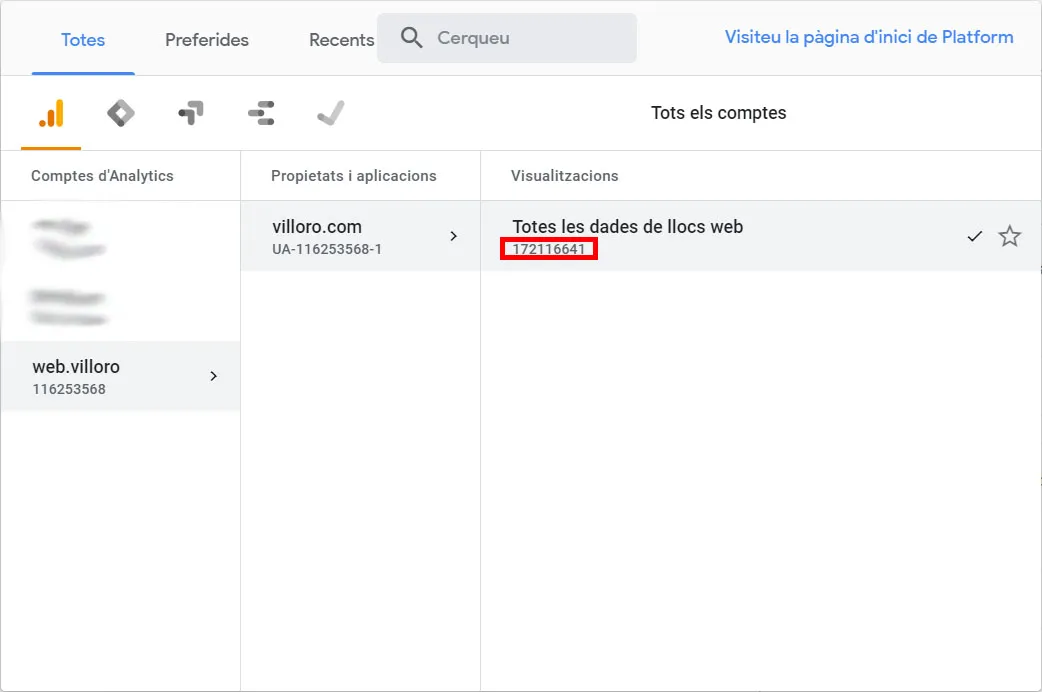
1.4. Profile ID
Get the ID that you will need to use with the API. There are three levels and the ID that you need to use is in the last one, the one with the red mark in the image.
2. Test the conection
You can run the test_conexion.py code to check that everything is working.
test_conexion.py
from datetime import date, timedelta
from apiclient.discovery import build
from oauth2client.service_account import ServiceAccountCredentials
# Those are the two constants you need to change
FILE_GA_KEY = "" path tho the key file
PROFILE = "" profile ID
def get_ga_service():
""" Connect to GA API service"""
credentials = ServiceAccountCredentials.from_json_keyfile_name(
FILE_GA_KEY, scopes=["https://www.googleapis.com/auth/analytics.readonly"]
)
# Build the service object.
return build("analytics", "v3", credentials=credentials)
def test():
""" Tests the conexion """
service = get_ga_service()
# Feel free to change those values
end = date.today()
dimensions = ["ga:date", "ga:deviceCategory"]
metrics = ["ga:users", "ga:sessions"]
start = end - timedelta(7)
# Query the API
kwa = {
"ids": "ga:{}".format(PROFILE),
"start_date": "{:%Y-%m-%d}".format(start),
"end_date": "{:%Y-%m-%d}".format(end),
"metrics": ",".join(metrics),
"dimensions": ",".join(dimensions),
"max_results": 20,
}
return service.data().ga().get(**kwa).execute()
Remeber to edit both FILE_GA_KEY and PROFILE constants using the values from the previous steps.
3. Building the ETL
3.1. Decide metrics and dimensions
Now is the time to decide what you want to download. There are two types of parameters metrics and dimensions.
- Dimensions are attributes of your data
- Metrics are quantitative measurements
You can check with Query explorer the possible values for both
of them and you can also try your queries.
3.2. Extract and transform the data
In this step I will descrive functions in the etl.py file.
The first thing to do is to create the Google Analytics service with:
etl.py
def get_ga_service(key_file_location=None):
""" Connect to GA API service"""
if key_file_location is None:
key_file_location = c.FILE_GA_KEY
scope = "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/analytics.readonly"
credentials = ServiceAccountCredentials.from_json_keyfile_name(
key_file_location, scopes=[scope]
)
# Build the service object.
return build("analytics", "v3", credentials=credentials)This function takes the default path of the Google Analytics key from the constants while allowing to pass a custom one.
Then to retrieve the actual data you should use get_da_df function.
etl.py
def get_ga_df(query_data, end=date.today(), service=None):
""" Retrieve GA data as dataframe """
if service is None:
service = get_ga_service()
dimensions = query_data["dimensions"].keys()
metrics = query_data["metrics"].keys()
start = end - timedelta(c.TIMEWINDOW)
# Query the API
kwa = {
"ids": "ga:{}".format(c.PROFILE),
"start_date": "{:%Y-%m-%d}".format(start),
"end_date": "{:%Y-%m-%d}".format(end),
"metrics": ",".join(metrics),
"dimensions": ",".join(dimensions),
"max_results": c.MAX_RESULTS,
}
data = service.data().ga().get(**kwa).execute()
# Create df from data obtained through the API
columns = [x["name"] for x in data["columnHeaders"]]
df = pd.DataFrame(data["rows"], columns=columns)
# Handle missing values
for x in dimensions:
df[x] = df[x].replace("(not set)", float("nan"))
# handle missing campaigns
if ("ga:adwordsCampaignID" in df.columns) and ("ga:campaign" in df.columns):
df.dropna(subset=["ga:adwordsCampaignID", "ga:campaign"], inplace=True)
# Rename columns
rename_dict = {i: x[0] for i, x in query_data["dimensions"].items()}
rename_dict.update({i: x[0] for i, x in query_data["metrics"].items()})
df = df.rename(index=str, columns=rename_dict)
# Transform types
for x in ["dimensions", "metrics"]:
df = u.fix_types(df, query_data[x].values())
log.info("Data read")
return dfThis function retrieves a pandas dataframe using the requested parameters.
After creating the raw dataframe it renames the columns using the dictionary QUERY_DATA from the constants.py file.
It will also change the columns types using the same dictionary.
So for example having:
constants.py
QUERY_DATA = {
"traffic_google": {
"dimensions": {"ga:date": ("date", "date"), "ga:deviceCategory": ("device", str)},
"metrics": {
"ga:users": ("users", int),
"ga:sessions": ("sessions", int),
"ga:bounceRate": ("bounce_rate", float),
},
},
}Will retrieve the ga:deviceCategory dimension, rename the column to device, and store it as a string.
Finally to run the ETL for all the tables in “QUERY_DATAthere is the functiondo_etl`:
etl.py
def do_etl():
""" Reads from GA, transforms the data and loads into mysql """
time0 = time()
for tablename, data in c.QUERY_DATA.items():
# Retrieve data from GA API
df = get_ga_df(data)
# Insert data into mysql
insert_into_mysql(df, tablename)
log.info("Data imported", time=time() - time0)This is what you should run every day. By default it will take the data from the last 7 days. This redundancy will mean that even if the ETL fails some day it can automatically retrieve the missing data the next day. In order to lose that it must fail 7 consecutive days.
And the last function is for retriving all old data. This is meant to only be used the first time.
etl.py
def import_old_stats(end=date.today()):
""" Imports old data up until 2017-01-01 """
# Load from 2017-01-01
while end > date(2017, 1, 1):
time0 = time()
start = end - timedelta(c.TIMEWINDOW)
log.info(f"Importing data from {start:%Y-%m-%d} to {end:%Y-%m-%d}")
for tablename, data in c.QUERY_DATA.items():
# Retrieve data from GA API
df = get_ga_df(data, end=end)
# Insert data into mysql
insert_into_mysql(df, tablename)
end -= timedelta(int(c.TIMEWINDOW) + 1)
log.info("Data imported", time=time() - time0)Right now it will download all data from 2017 until today.
3.3. Load the data
In this example amb going to show how to insert the data into MySQL.
All this code is from sql.py file.
3.3.1. Handling duplicated data
The idea is that the ETL can be run more than once without creating duplicated data. This is also important since the ETL is designed with redundancy to allow some failures so it is needed to handle duplicates.
There are two approaches to this problem:
3.3.1.1. Using date as identifier
Every time you download data you will have a dataframe with info of the last 7 days. In order to avoid duplicates you can simply delete all rows that have data within the same days.
3.3.1.2. Use all ‘index’ columns
The other approach is to load all existing data and concatenate with the new one.
This dataframe will have duplicates but they can be deleted with the drop_duplicates pandas function.
To do so you need to specify which are the columns that define a unique entry.
This solution is less efficient since it will need to load all existing data and this can be time consuming.
3.3.2. Load code
The first thing to do is to create the SQL Alchemy engine for MySQL.
For other SQL engines check the SQL Alchemy with python.
sql.py
def _get_mysql_engine():
""" Get MySQL SQLAlchemy engine """
return sa.create_engine(
sa.engine.url.URL(
drivername="mysql+pymysql",
username="username", # Change that!!
password="password", # Change that!!
host="host", # Change that!!
port=c.PORT,
database=c.DATABASE,
),
encoding="utf-8", # Since there will be some japanse chars
)Using the create_engine and engine.url.URL functions from SQLAlchemy is the most elegant way to create the engine.
To retrieve a table you can use:
sql.py
def get_df_mysql(tablename, columns="*", engine=None):
""" Retrieves one table from MySQL """
if engine is None:
engine = _get_mysql_engine()
query = "SELECT {} FROM {}".format(columns, tablename)
with engine.connect() as connection:
return pd.read_sql_query(query, connection)And finally the code to insert the data handling the duplicates:
sql.py
def insert_into_mysql(df, tablename, cols_id=None, engine=None):
"""
Insert dataframe into mysql.
If date column is present it will delete all rows that are in the same
date range as df to be inserted. Else it will truncate the sql table.
Args:
df: dataframe to insert
tablename: name of the table
cols_id: allow dropping duplicates using those columns instead of deleting all
engine: sql_alchemy engine
"""
if engine is None:
engine = _get_mysql_engine()
# If date is present, delete rows of same date
if "date" in df.columns:
# Transform date to string to avoid SQL problems
df["date"] = pd.to_datetime(df["date"]).dt.strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
# Get all dates present in df to insert
dates = df["date"].unique()
# Delete data of same dates as the data that will be inserted
sentence = c.DELETE.format(table=tablename, dates="','".join(dates))
with engine.connect() as connection:
connection.execute(sentence)
# Truncate all data or keep non duplicated
else:
# Try to merge with existing data
if cols_id is not None:
# retrieve existing data
df_prev = get_df_mysql(tablename, engine=engine)
# Drop duplicated data
df = pd.concat([df, df_prev], sort=False)
df.drop_duplicates(subset=cols_id, inplace=True)
with engine.connect() as connection:
connection.execute(c.TRUNCATE.format(tablename))
# Insert into SQL
df.to_sql(name=tablename, con=engine, if_exists="append", index=False)This code will check if the date column is present.
If it is it will handle duplicates using it, if not it will use the other approach.
And with all that you can create an ETL to load data from Google Analytics.



